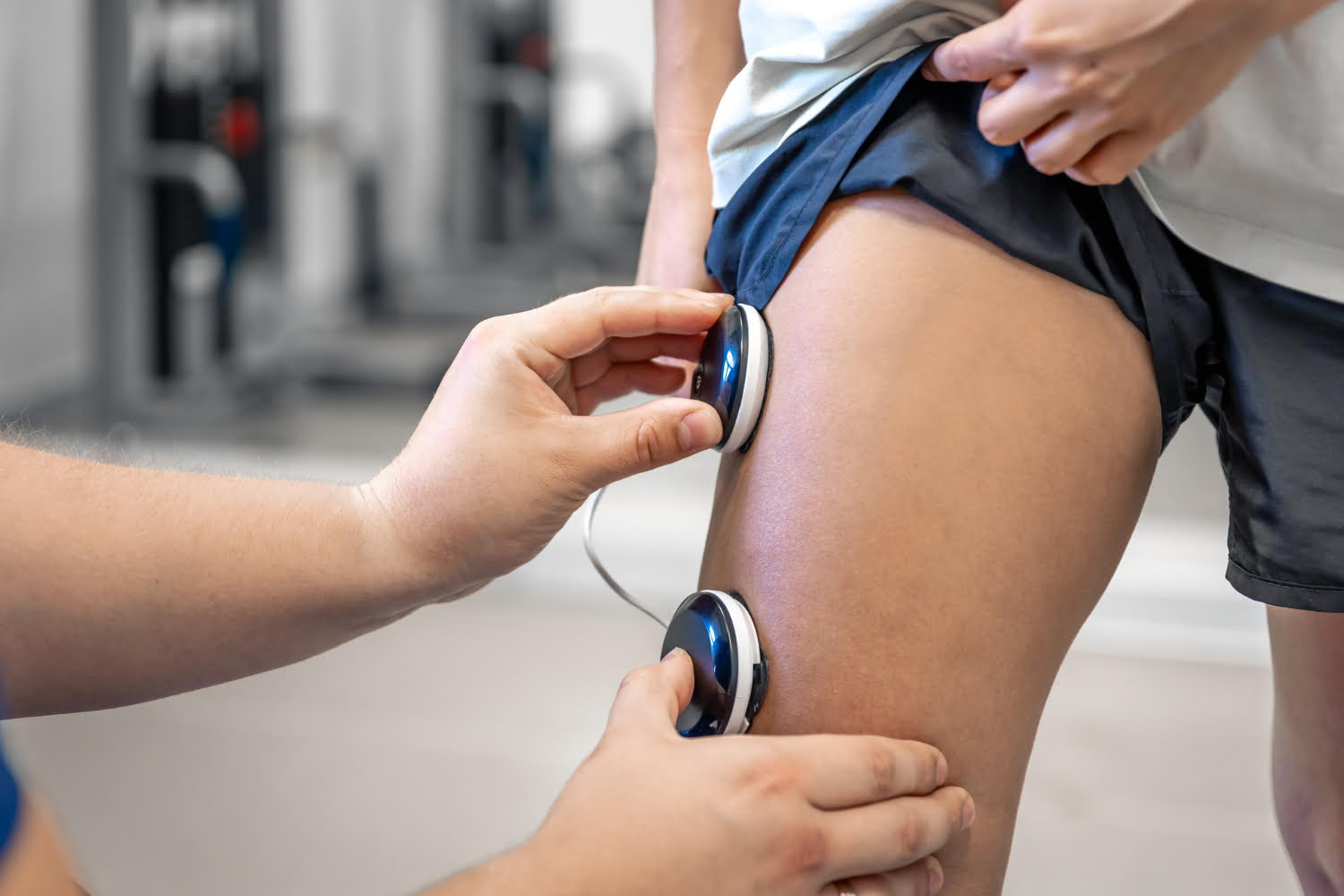
The application of low-frequency neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) has shown its ability to increase energy expenditure compared to conventional low-intensity exercises. In this sense, the results of a research have recently been published in which the authors studied the effects of 1 hour of NMES in lower limbs, comparing the responses with those obtained by walking in obese patients.
Electrostimulation to Lose Weight.
The results showed that 1 hour of NMES was associated with an increase in Vo2, reaching an average of 47% V02 max, with an average heart rate of 114 beats per minute and an energy expenditure of 318 kcal/h. Electrostimulation increased carbohydrate metabolism (more than walking) but not fat metabolism (less than walking). The lactate concentration during NMES reached 3.5 mM while walking only reached 1.5 mM.
Electrostimulation has been shown to have benefits in training and sports performance and with this study it clearly demonstrates its positive effect for losing weight in cases of notable overweight, cases in which there are often mobility limitations, which is an important limiting factor when it comes to of exercising.

 Workout
Workout
 Meditation
Meditation





 Contact Us
Contact Us