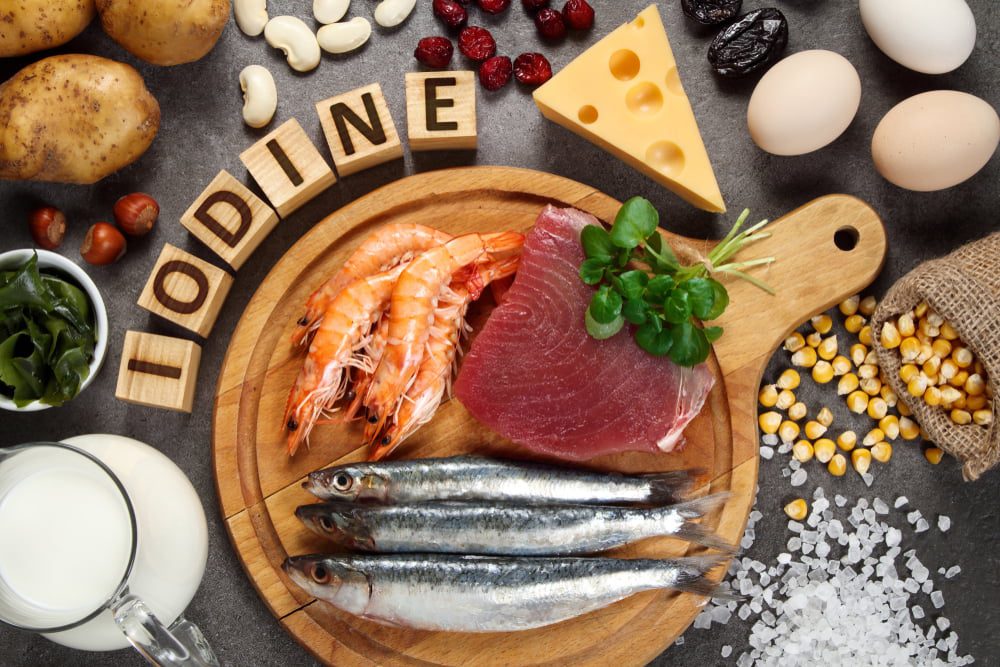
Iodine is an essential mineral for the human body, and a lack of it can cause a range of health issues. Low iodine intake can lead to thyroid problems, mental impairment, infertility, and even cretinism in extreme cases. In this article, we will discuss the various risks associated with low iodine intake and what can be done to prevent them.
What can happen due to low iodine intake?
1. Goiter: A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland due to a lack of iodine in the diet.
2. Mental retardation: Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can cause mental retardation in children.
3. Poor growth: Without sufficient iodine, children may experience stunted physical and mental growth.
4. Weakened immune system: Low iodine levels can weaken the immune system, making a person more susceptible to infections.
5. Hearing loss: In infants, a lack of iodine can cause hearing loss.
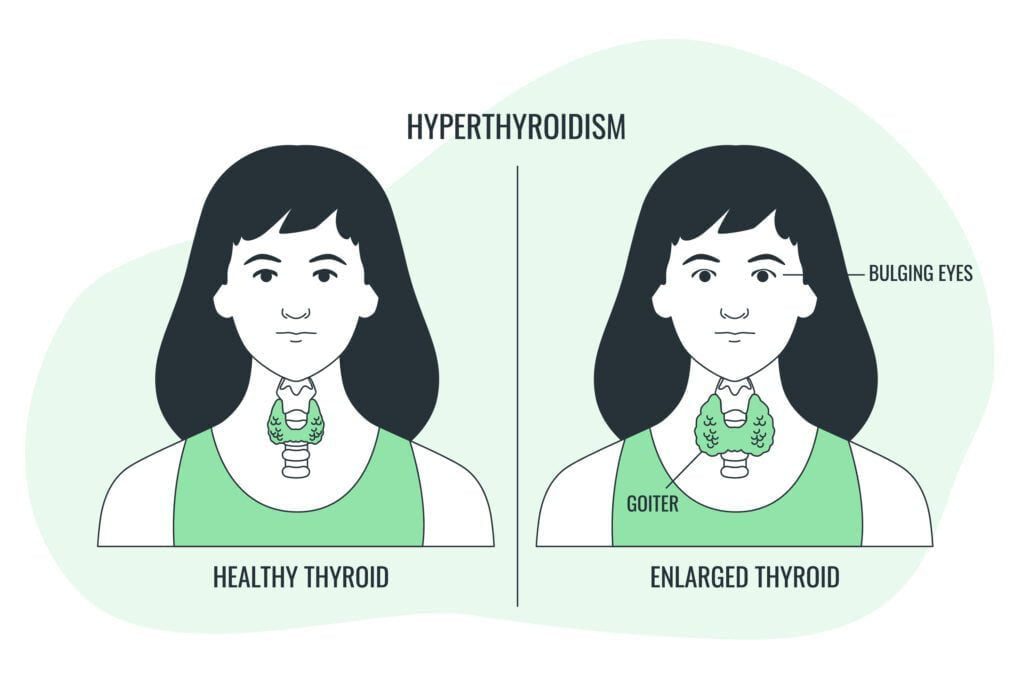
6. Thyroid problems: Low iodine can lead to thyroid problems such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
7. Infertility: In both men and women, iodine deficiency can cause infertility.
8. Cognitive impairment: Low levels of iodine can lead to impaired cognitive development in children and adults.
9. Dry skin: Iodine is necessary for healthy skin, and a lack of it can cause dry skin and other skin problems.
10. Heart problems: Low iodine can lead to an irregular heartbeat, known as arrhythmia, as well as other heart problems.
How to prevent negative effects due to low iodine intake?
1. Ensure that you are consuming a balanced diet that includes foods that are rich in iodine, such as iodized salt, dairy products, seafood, and some types of seaweed.
2. Take a multivitamin that contains iodine.
3. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it is especially important to ensure that your diet contains enough iodine as it is essential for the development of your baby’s brain.
4. Discuss your iodine intake with your doctor and consider taking an iodine supplement if necessary.
5. Avoid processed foods, which are often stripped of essential nutrients, including iodine.
6. Avoid foods that contain goitrogens, which are substances that interfere with the body’s ability to absorb iodine.
7. Limit your exposure to environmental toxins, such as radiation, which can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb iodine.
Bottom Line.
Low iodine intake can have detrimental effects on both physical and cognitive development. It can lead to various health issues such as goiter, hypothyroidism, and impaired brain function. Pregnant women and infants are particularly vulnerable to the adverse consequences of iodine deficiency, which can result in severe developmental abnormalities.
It is crucial that individuals maintain an adequate iodine intake through the consumption of iodine-rich foods or the use of iodized salt. Public health initiatives and educational programs are essential to raise awareness about the importance of iodine and ensure the prevention and management of iodine deficiency disorders.
By addressing this nutritional deficiency, we can promote overall health and well-being for individuals across all age groups.

 Workout
Workout
 Meditation
Meditation





 Contact Us
Contact Us





